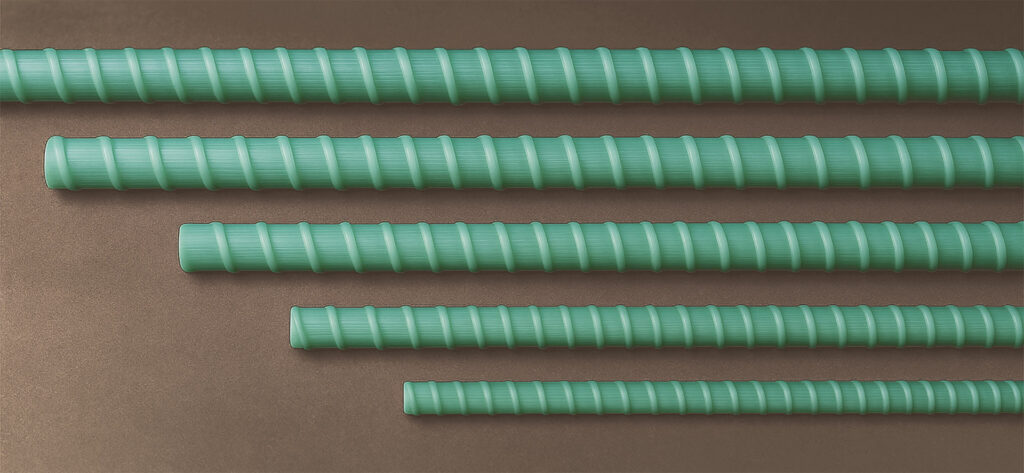
Next-Generation Rebar Alternative: GFRP

Steel vs GFRP Service Life Comparison
Category
Steel Rebar
GFRP Rebar
1. Service life in normal environments
(with proper maintenance)
Steel Rebar
50 – 100 years
GFRP Rebar
Over 100 years
2. Service Life in Harsh Environments
(marine / high-salinity areas)
Steel Rebar
20 – 40 years
GFRP Rebar
Over 100 years
3. Main Cause of Reduced Service Life
Steel Rebar
Corrosion and crack
GFRP Rebar
None
Four Key Advantages of GFRP Rebar
25 %
0 %
30 %
100 Y

Productivity & Workability
Lightweight
About one-fourth the weight of steel rebar, making handling and transport much easier.
Faster Installation
Reduces installation time by up to 30%.
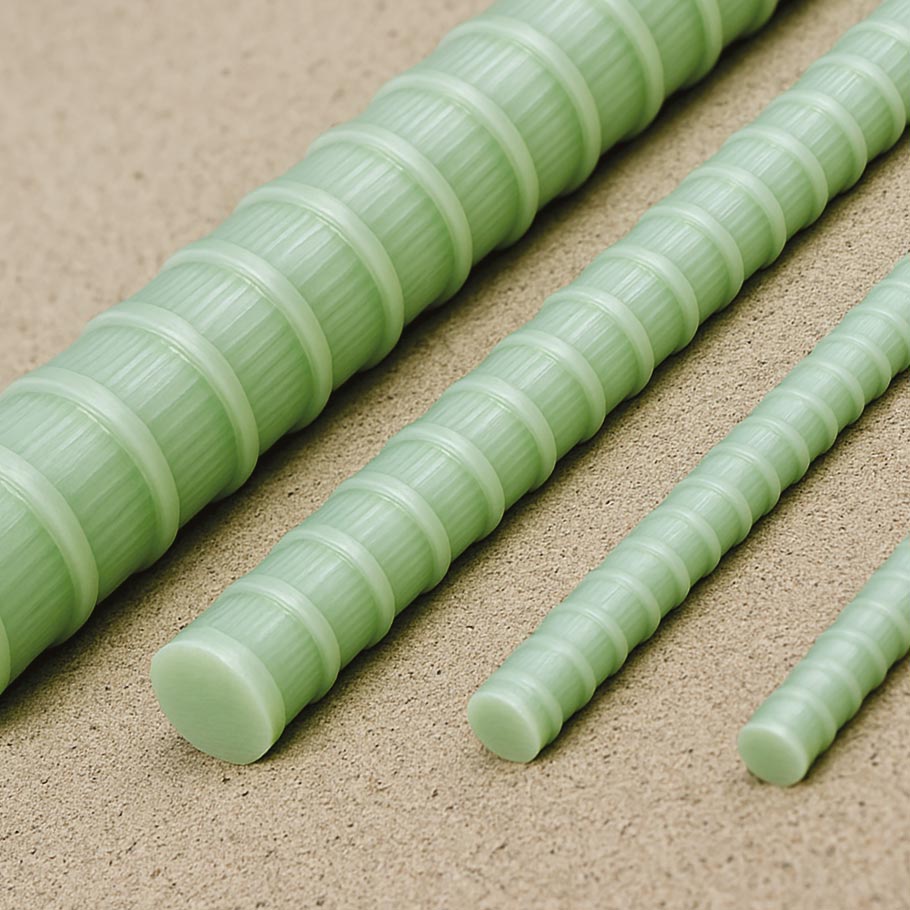

Safety
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Does not rust even when exposed to water, salts, or chemicals, completely preventing rebar corrosion problems.
Extended Service Life
Extends the lifespan of structures in corrosive environments by over 100 years.

Environmental Sustainability
Low Carbon & Energy Footprint
Requires less energy during production than steel and produces far lower CO2 emissions.
Sustainable Infrastructure
Longer structural lifespan reduces material waste and resource consumption.

Cost Efficiency
Reduced Life-Cycle Cost (LCC)
Minimizes long-term maintenance expenses due to excellent corrosion resistance
Low Maintenance Requirement
Corrosion resistance significantly cuts repair and upkeep costs.
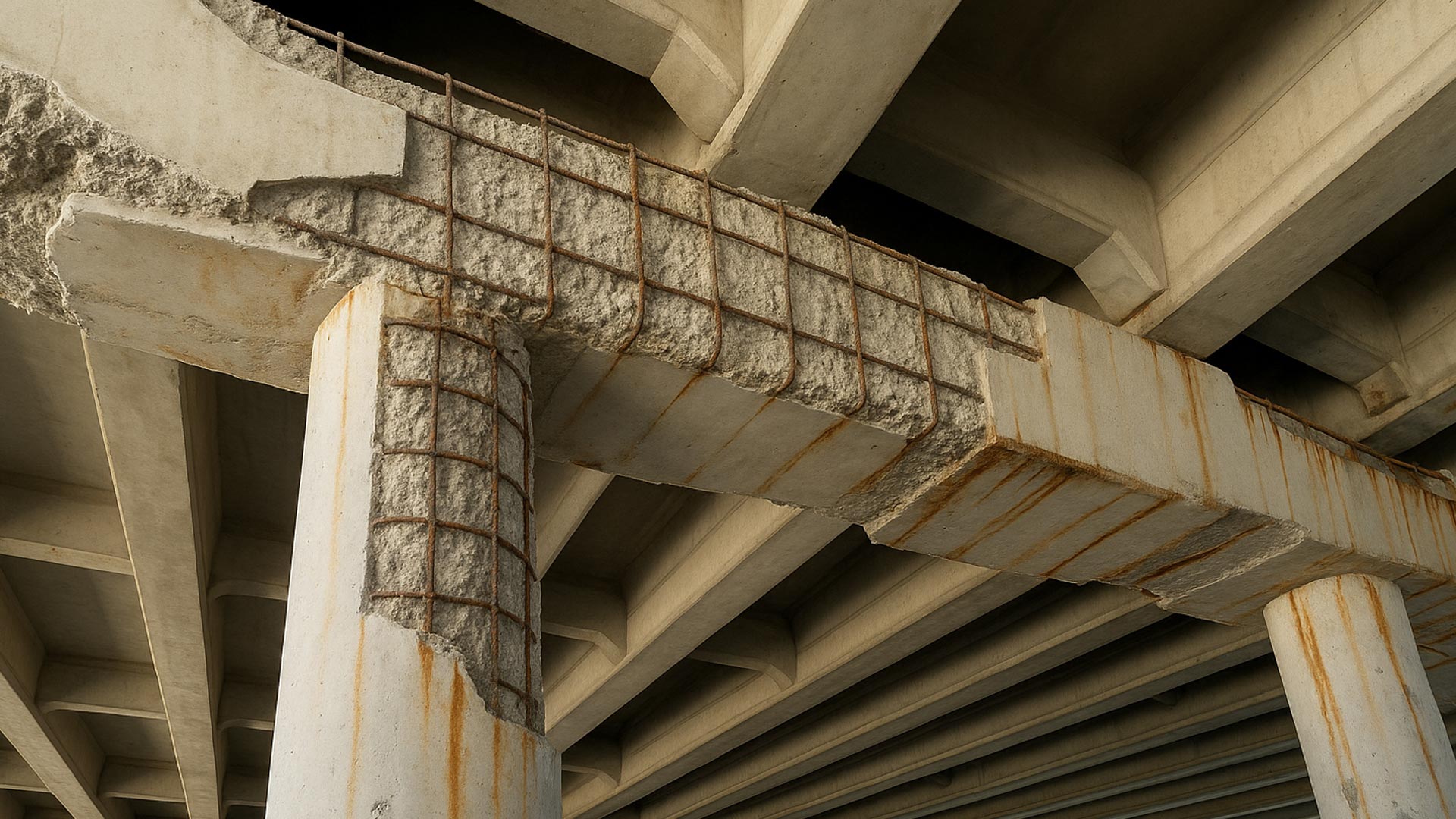
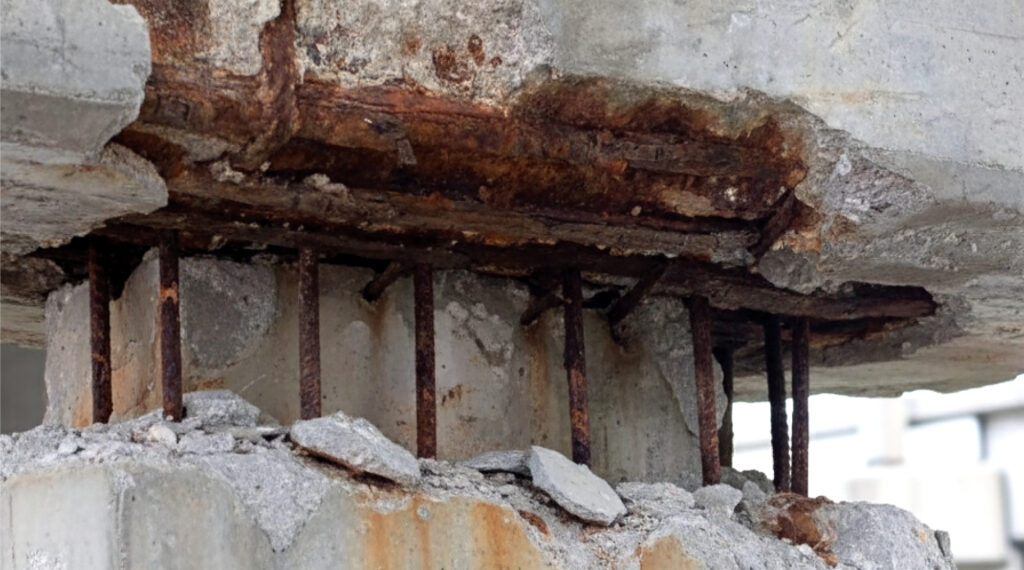
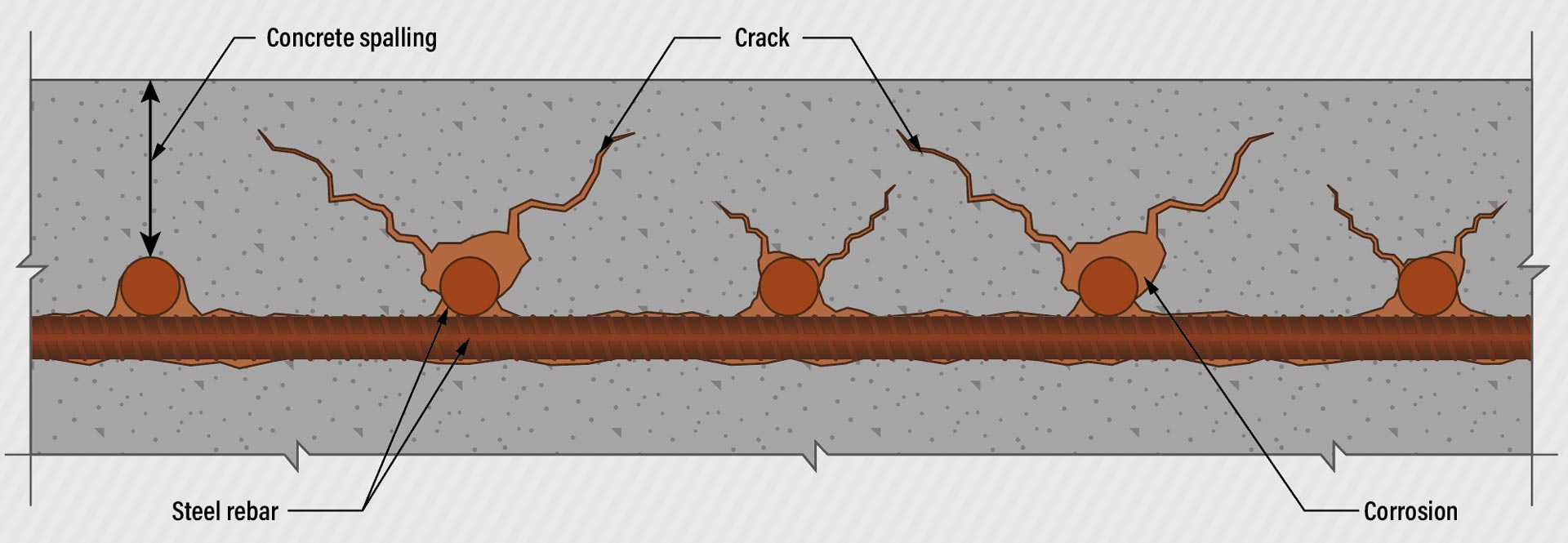
As steel corrodes, the rust that forms expands in volume, creating internal tensile stress within the concrete.
This stress leads to cracking, spalling, and delamination. A phenomenon known as concrete deterioration due to corrosion.
To build safer, longer-lasting, and more sustainable concrete structures, GFRP Rebar is being rapidly adopted across a wide range of applications, establishing itself as the new standard for future infrastructure.